The Evolution of Security Systems: From Locks to AI
Security systems have come a long way from simple mechanical locks and guards to today's sophisticated, AI-powered surveillance and protection technologies. Driven by technological advancements, changing societal needs, and emerging threats, the evolution of security systems reflects humanity’s constant pursuit of safety and peace of mind.
The Early Days: Mechanical Locks and Physical Barriers
The concept of security dates back thousands of years. Ancient civilizations used rudimentary locks made of wood and metal to safeguard property. The earliest known lock, dating back to 4,000 years ago in Egypt, operated on a simple pin tumbler mechanism. Fortresses, city walls, and guarded gates were common methods of physical protection throughout history.
By the 18th and 19th centuries, mechanical lock design had become more sophisticated. Locksmiths like Linus Yale Sr. and Jr. revolutionized the field with the invention of the modern pin tumbler lock, setting the foundation for residential and commercial security.
The 20th Century: The Rise of Electronic Security
The 20th century marked the beginning of electronic security systems. In the 1960s, the first monitored alarm systems gained popularity, allowing homeowners to alert local authorities in the event of a break-in. Closed-circuit television (CCTV) began appearing in public and private spaces during the 1970s, initially used for military and government surveillance.
As technology advanced, the 1980s and 1990s saw the integration of motion detectors, infrared sensors, and electronic access control systems. These technologies began appearing in banks, office buildings, and eventually, private homes. The use of keycards, PIN codes, and early biometric systems (like fingerprint scanners) started to replace traditional keys in high-security environments.
The 21st Century: Smart Systems and the Internet of Things (IoT)
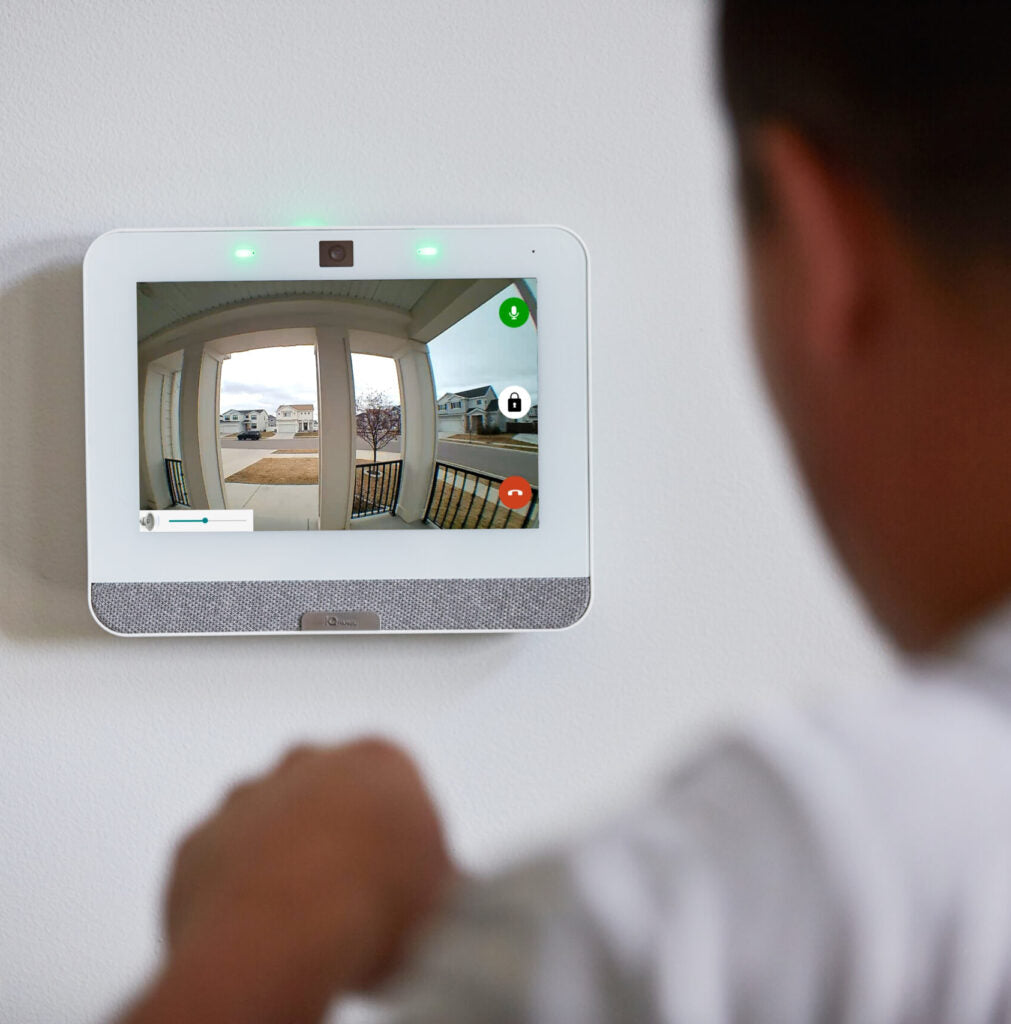
The digital age transformed security once again. The emergence of smart home technology and the Internet of Things (IoT) in the early 2000s made advanced security accessible to the average consumer. Modern systems now include:
-
Smart locks and video doorbells that can be controlled remotely via smartphones.
-
Wireless alarm systems with cloud-based monitoring.
-
AI-powered surveillance cameras capable of facial recognition, behavior analysis, and real-time alerts.
-
Integration with virtual assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant for voice-activated control.
These innovations allowed users to monitor and control their home security from anywhere in the world, increasing convenience and responsiveness.
Current Trends: AI, Automation, and Cybersecurity
Today’s security systems are increasingly intelligent. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms allow systems to differentiate between normal and suspicious activity, reducing false alarms and enhancing accuracy. Smart analytics can predict potential threats based on patterns of behavior or historical data.
In addition, cybersecurity has become a critical component. As physical security systems become more digital and connected, they are vulnerable to hacking and cyber threats. Modern security now includes firewalls, encrypted communication, and software updates to safeguard against both physical and digital breaches.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Security
The future of security systems will likely involve deeper integration with AI, greater reliance on cloud computing, and more robust privacy safeguards. We may see widespread adoption of:
-
Biometric-only access control
-
Autonomous drones for perimeter surveillance
-
Predictive threat analysis
-
Blockchain-based identity management
As threats evolve, so will the technologies that protect us. From ancient locks to intelligent systems, the journey of security innovation continues—reshaping how we think about safety in an increasingly interconnected world.